NOTICE
ANSM - Last updated: 26/07/2017
Name of the medicinal product
POLARAMINE 2 mg, scored tablet
Dexchlorpheniramine maleate
framed
Please read this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because it contains important information for you.
You should always take this medication exactly as prescribed in this leaflet or by your doctor or pharmacist.
· Keep this leaflet. You might need to read it again.
· Ask your pharmacist for advice or information.
· If you experience any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This also applies to any side effects not mentioned in this leaflet. See section 4.
· You should contact your doctor if you experience no improvement or feel less well after treatment.
What is in this leaflet?
1. What is POLARAMINE 2 mg, scored tablet and in which cases it is used?
2. What information should I take before taking POLARAMINE 2 mg scored tablet?
3. How to take POLARAMINE 2 mg tablet scored?
4. What are the possible side effects?
5. How to store POLARAMINE 2 mg scored tablet?
6. Package contents and other information.
1. WHAT IS POLARAMINE 2 mg scored tablet AND WHAT IT IS USED FOR?
Pharmacotherapeutic group - ATC code: ANTIHISTAMINIC FOR SYSTEMIC USE
(R. Respiratory system)
(D. Dermatology)
This medication contains an antihistamine, dexchlorphenamine.
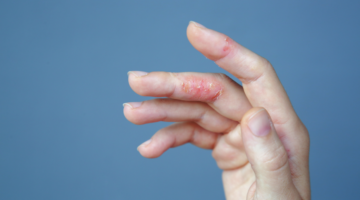
It is indicated in the symptomatic treatment of allergic manifestations such as:
· rhinitis (eg hay fever, non-seasonal rhinitis ...),
· conjunctivitis (inflammation of the eye),
· urticaria
In adults and children over 6 years of age.
2. BEFORE YOU TAKE POLARAMINE 2 mg tablet scored?
Never take POLARAMINE 2 mg scored tablet:
· if you are allergic to the active substance or to any of the other ingredients of this medication mentioned in section 6.
· If you have difficulty urinating from prostatic or other sources,
· If you have some forms of glaucoma (increased pressure in the eye),
· For children under 6 years due to the pharmaceutical form
This medication is GENERALLY NOT RECOMMENDED unless your doctor advises otherwise, in case of breast-feeding.
IN CASE OF DOUBT, IT IS ESSENTIAL TO ASK FOR THE OPINION OF YOUR DOCTOR OR YOUR PHARMACIST.
Warnings and Precautions
Talk to your doctor or pharmacist before taking POLARAMINE 2 mg scored tablet.
This medication only treats the manifestations of your allergy. Their origin must be sought.
If symptoms persist or worsen, SEEK YOUR DOCTOR.
This medicine contains lactose. Its use is not recommended in patients with galactose intolerance, Lapp lactase deficiency or glucose or galactose malabsorption syndrome (rare hereditary diseases).
In case of long-term liver or kidney disease, CONSULT YOUR DOCTOR so that he can adapt the dosage.
Taking this medication requires a MEDICAL ADVICE in the elderly:
· predisposed to constipation, dizziness or drowsiness,
· having prostate disorders;
PREVENT YOUR DOCTOR before taking this antihistamine.
Refrain from alcoholic beverages or medication containing alcohol during the course of treatment.
IN CASE OF DOUBT, DO NOT HESITATE TO ASK FOR THE OPINION OF YOUR PHYSICIAN OR YOUR PHARMACIST.
Children and Youth
Not applicable.
Other medicines and POLARAMINE 2 mg, scored tablet
Inform your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking, have recently taken or may take any other medicines.
This medicine contains dexchlorphenamine. Other medicines contain it. Do not combine them in order not to exceed the maximum recommended doses ( see Dosage ).
POLARAMINE 2 mg, scored tablet with food, beverages and alcohol
Not applicable.
Pregnancy and breast feeding
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant or plan a pregnancy, ask your doctor for advice or pharmacist before taking this medication.
Pregnancy
It is possible to take this medication during the first two trimesters of your pregnancy. Use during the 3rd trimester should only be considered if necessary and limited to one-time use.
At the end of pregnancy, abuse of this drug may cause adverse effects in the newborn.
feeding
This drug passes into breast milk. It is therefore not recommended for breastfeeding women.
Ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before taking any medicine.
Driving and using machines
Attention is drawn, especially to vehicle drivers and machine users, on the possibilities of drowsiness or decreased vigilance associated with the use of this medication.
This is exacerbated by the use of alcoholic beverages or alcohol-containing medications.
It is best to start this treatment one night.
POLARAMINE 2 mg scored tablet contains lactose
3. HOW TO TAKE POLARAMINE 2 mg scored tablet?
Always take this medication exactly as prescribed by your doctor or pharmacist. Check with your doctor or pharmacist if in doubt.
Dosage
RESERVED FOR ADULTS AND CHILDREN OVER 6 YEARS.
Adult and child over 12 years: 1 tablet, 3 to 4 times a day.
Children from 6 to 12 years: 1/2 tablet, 2 or 3 times a day.
Method and route of administration
Oral use.
The tablets should be swallowed with a glass of water.
Frequency of Administration
They must be spaced at least 4 hours apart.
Given the sleepiness effect of this medication, it is best to start treatment one night.
Duration of treatment
The duration of treatment should be short.
Always take this medication exactly as prescribed in this leaflet or as directed by your doctor or pharmacist. Check with your doctor or pharmacist if in doubt.
If you take more POLARAMINE 2 mg tablets than you should have
Immediately consult your doctor or pharmacist.
If you forget to take POLARAMINE 2 mg, scored tablet
Not applicable.
If you stop taking POLARAMINE 2 mg, scored tablet
Not applicable.
If you have any further questions on the use of this medication, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4. WHAT ARE POSSIBLE SIDE EFFECTS?
Like all medicines, this medicine may cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
· Some side effects require STOPPING IMMEDIATELY TREATMENT AND WARNING A DOCTOR:
o Allergic reactions:
§ rash type (erythema, eczema, purpura, urticaria);
§ angioedema (urticaria with sudden swelling of the face and neck, which can cause respiratory discomfort);
§ anaphylactic shock;
o Significant decrease in white blood cells in the blood, which may be manifested by the onset or recurrence of fever with or without signs of infection;
o Abnormal decrease in platelets in the blood, which can result in nose bleeds or gums.
· Other side effects may include:
o Drowsiness, decreased vigilance, more marked at the beginning of treatment.
o Memory or concentration disorders, dizziness (more common in the elderly),
o Motor incoordination, tremors,
o Confusion, hallucinations,
o Dry mouth, visual disturbances, urine retention, constipation, palpitations, low blood pressure.
· More rarely, signs of excitement (agitation, nervousness, insomnia) may occur.
Declaration of side effects
If you experience any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This also applies to any side effects not mentioned in this leaflet. You can also report adverse reactions directly via the national reporting system: National Agency for the Safety of Medicines and Health Products (ANSM) and network of Regional Centers of Pharmacovigilance - Website: www.ansm.sante.fr
By reporting adverse reactions, you are helping to provide more information about the safety of the drug.
5. HOW TO STORE POLARAMINE 2 mg scored tablet?
Keep this medicine out of the reach and sight of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date which is stated on the carton after {EXP}. The expiry date refers to the last day of that month.
No special storage conditions.
Do not throw any medicines into drains or rubbish. Ask your pharmacist to remove any medications you are no longer using. These measures will help protect the environment.
6. PACKAGE CONTENTS AND OTHER INFORMATION
What POLARAMINE 2 mg contains, scored tablet
· The active substance (s) is (are):
Dexchlorpheniramine Maleate ............................................... .......................................... 2 mg
For a scored tablet
· The other components are: lactose monohydrate, corn starch, pregelatinized maize starch, magnesium stearate
What is POLARAMINE 2 mg, scored tablet and contents of the pack
This medication is in the form of a scored tablet. Box of 20, 28 or 30.
Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
Marketing Authorization Holder
BAYER HEALTHCARE SAS
220 avenue de la Recherche
59120 LOOS
LA FRANCE
Marketing Authorization Operator
BAYER HEALTHCARE SAS
33 rue de l'Industrie
74240 GAILLARD
LA FRANCE
Maker
SCHERING-PLOUGH LABO NV
INDUSTRIEPARK 30,
2220 HEIST-OP-DEN-BERG
Belgium
Or
AESICA PHARMACEUTICALS GMBH
ALFRED-NOBEL-STRASSE 10
40789 MONHEIM
GERMANY
Names of the medicinal product in the Member States of the European Economic Area
Not applicable.
The last date on which this leaflet was revised is:
[to be completed later by the holder]
Other
Detailed information on this medicine is available on the ANSM website (France).