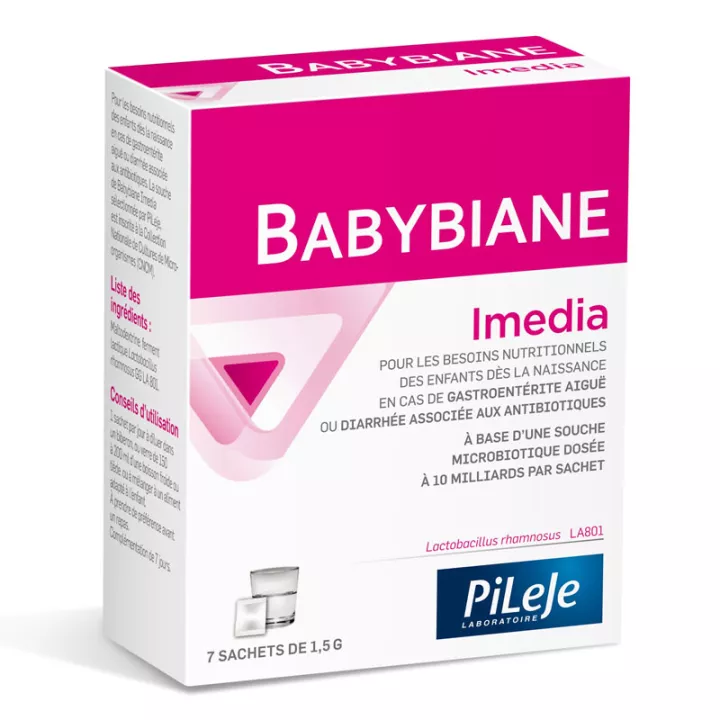
What is Babybiane Immédiat Diarrhée bébé en Sachets probiotique Pileje used for?
Babybiane Imedia is an effective solution to meet the nutritional needs of children in the event of:
- acute gastroenteritis
- antibiotic-associated diarrhea
It can be used from birth to 4 years of age.
Diarrhea in babies can be a real challenge for parents, but with Babybiane Immédiat, you have an effective solution to help your child recover quickly.
Babybiane Immédiat is specially designed to meet the nutritional needs of children suffering from diarrhoea, whether it be acute gastroenteritis or diarrhoea associated with antibiotics. This solution can be used from birth to 4 years of age, providing a suitable solution for toddlers.
Each sachet of Babybiane Immédiat contains a high concentration of Lactobacillus rhamnosus, a probiotic recognized for its beneficial effects on intestinal health. With 10 billion Lactobacillus rhamnosus per sachet, this formula offers effective support to restore the balance of your baby's intestinal flora and promote rapid recovery.
The probiotics in Babybiane Immédiat work quickly to relieve the symptoms of diarrhoea in babies. By reducing the duration of diarrhoea and improving lactose digestion, this supplement helps restore your child's intestinal comfort and promote rapid recovery.
As well as relieving the symptoms of diarrhoea, Babybiane Immédiat also boosts your baby's immunity after taking antibiotics. What's more, this supplement can alleviate manifestations of infantile colic and symptoms of atopic dermatitis, offering overall relief for your child.
Developed by Pileje Laboratories, Babybiane Immédiat benefits from recognized expertise in infant nutrition and intestinal health. This probiotic solution has been carefully formulated to offer maximum efficacy, while being adapted to the specific needs of toddlers.
1 sachet = 10 billion Lactobacillus rhamnosus
Is your baby suffering from diarrhea due to acute gastroenteritis or antibiotics? Pileje Laboratories have found the solution to help your little one get back to full health as quickly as possible!
- Relieves manifestations of infantile colic
- Reduces the duration of diarrhea, whether or not associated with antibiotics
- Improves lactose digestion
- Boostsimmunity after antibiotics
- Alleviates symptoms of atopic dermatitis
We also offer Amande Douce Huile Gifrer 56 ml, particularly recommended for dry or irritated skin, as well as during pregnancy to prevent and/or reduce stretch marks.
How to use these sachets
1 Babydiane Imedia sachet a day, to be diluted in a bottle or glass of water or cold milk, or mixed with a food suitable for the child. Can be diluted in an oral rehydration solution. Best taken before a meal.
Give your opinion on the advice for use and dosage of Babybiane Immédiat Diarrhée bébé 7 Sachets probiotique Pileje with our partner Verified opinions after your purchase.
What are the precautions for use?
Babybiane Imedia should only be used under medical supervision.
What is its composition?
Babybiane Imedia provides 1 microbiotic strain at 10 billion per sachet: Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG LA 801. Maltodextrin, Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG LA 801 lactic ferment.
Packaging:
Box of 7 sachets.
Our advice and expert opinions in pharmacy
Focus on Lactobacillus Rhamnosus:
This well-known probiotic has been the subject of numerous studies proving its beneficial role on our intestinal flora. In fact, this strain fights against the development of pathogenic bacteria, restoring our inner balance. That's why it's so useful in cases of gastroenteritis. It also combats intestinal permeability, which is why it can be used in cases of irritable bowel syndrome.
In addition to its action on intestinal balance, this strain is also effective in cases of vaginal flora imbalance, particularly bacterial vaginosis.